How to stop gums from bleeding
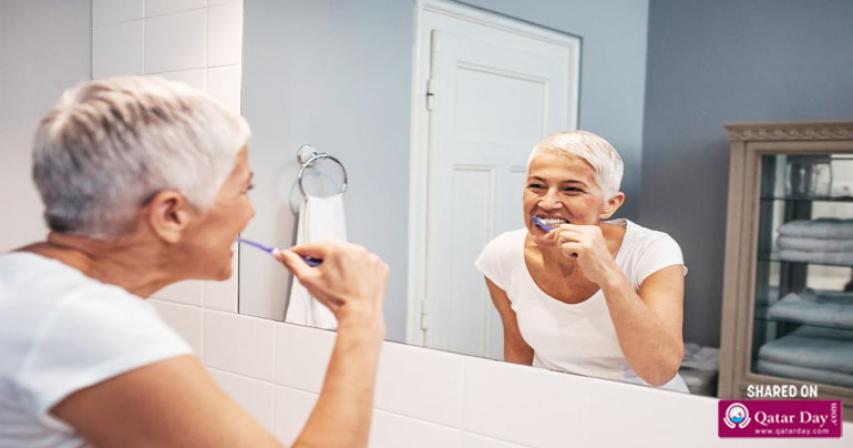

In most cases, people can treat minor gum bleeding at home. Good oral hygiene and natural remedies can treat and prevent gum bleeding.
Gum bleeding is common and is typically not serious. A person may notice some blood after brushing their teeth or flossing, which can irritate sensitive gums.
The most common reason a person's gums bleed is because of plaque or tartar buildup. These substances allow bacteria to grow along the gum line. Good oral hygiene can prevent sensitivity and bleeding.
Common causes of sensitive or bleeding gums include:
- not brushing the teeth often enough, or at least twice a day
- using a toothbrush that is too hard or stiff
- using a frayed, worn toothbrush that no longer cleans effectively
- using dental floss roughly, instead of gently pushing it down and hugging the sides of each tooth
- taking certain medicines, such as aspirin, blood thinners, or ibuprofen
- having gingivitis, or early-stage gum disease
Try the following methods to stop gums from bleeding and to prevent the bleeding from coming back again.
1. Using gauze
- Practicing good oral hygiene can help treat bleeding gums.
- Practicing good oral hygiene can help treat bleeding gums.
- As with bleeding anywhere else on the body, people can help stop the bleeding by immediately holding a clean, damp gauze against the affected area.
Gently press the gauze in place until the blood has stopped flowing.
People with a weakened immune system or another medical condition may find that their gums take a long time to stop bleeding. Speak to a dentist about the best way to stop the blood flow.
2. Using ice
Hold a cool compress, a small ice pack, or an ice cube against swollen, bleeding gums to help soothe them.
Ice packs are especially helpful to soothe minor mouth injuries that cause swelling, such as cuts and scrapes. They can also help reduce pain and swelling caused by gingivitis.
Use ice for 10 minutes at a time and take 10-minute breaks. If the bleeding does not stop, some people may consider calling a doctor.
3. Using mouthwash
Antibacterial mouthwashes can both treat and prevent bleeding gums. They kill bacteria and reduce inflammation to soothe sore, swollen, and bleeding gums.
Mouthwash can also treat and prevent gingivitis, which is a common cause of bleeding gums.
Common active ingredients in mouthwashes include:
chlorohexidine
hydrogen peroxide
Keep mouthwash on hand to treat bleeding gums when they occur. People can buy mouthwash from drug stores or choose between brands online.
4. Using a warm salt rinse
Rinsing the mouth with salt water can help reduce bacteria and speed up healing times. According to the American Dental Association (ADA), a person can make an oral salt rinse by adding half a teaspoon of salt to 8 ounces of warm water.
Swish the salt rinse around the mouth to cleanse the area and then spit the liquid out. Repeat this several times a day, or according to instructions from your dentist.
5. Applying a turmeric paste
Turmeric with turmeric paste
Scientific evidence does not support turmeric paste as a treatment for bleeding gums.
Turmeric has natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. Applying a turmeric paste to the gums may improve the symptoms of gingivitis and bleeding gums.
However, there is currently no reliable scientific evidence that states turmeric has any effect on gum disease or bleeding gums.
One small-scale study compared the effects of curcumin, the active ingredient in turmeric, with the effects of chlorhexidine in oral hygiene. The researchers found similar anti-inflammatory effects in people who used these gels for 10 minutes a day twice a day.
Turmeric is yellow, but it should not stain a person's teeth as long as they rinse well after using it. Some people use turmeric as a tooth whitening agent, especially when combined with baking soda. However, there is no evidence for this remedy's effectiveness.
6. Using the right toothbrush
If a person has sensitive gums, they can opt for a toothbrush labeled as extra soft or sensitive. Firm or medium toothbrushes are too rough on the gums.
The ADA recommend that people use a toothbrush with soft bristles for 2 minutes twice a day. They say that both manual and electric toothbrushes are effective.
Replace toothbrushes every 3 to 4 months, or sooner if the bristles look frayed.
7. Flossing every day, but be gentle
Starting a new flossing habit can cause bleeding at first. The gums may not be used to the stimulation. However, after a few days of consistent flossing, the bleeding should stop.
Regular flossing improves overall gum health and should reduce gum bleeding over time.
8. Avoiding smoking
Smoking is a major cause of gum disease, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Smoking harms the body's immune system, meaning the body is less able to fight off the bacteria that naturally stick to the gums.
Once the gums are damaged, smoking makes it harder for the body to heal its tissues.
Quitting smoking benefits the whole body, and greatly increases the health of a person's mouth and gums. People often notice improvements in their oral health quickly after stopping smoking.
9. Trying oil pulling
Oil pulling is an ancient Ayurvedic medicine practice. It involves swishing a specific oil in the mouth for up to 20 minutes, then spitting it out. Proponents claim that it can whiten teeth and improve oral health.
Though some people may find that oil pulling helps them, the ADA do not recommend it for dental hygiene because there is a lack of scientific evidence into its effectiveness. Experts suggest that oil pulling cannot replace regular brushing and flossing.
Some limited, small-scale research suggests that oil pulling is more effective than a placebo at controlling plaque levels in the mouth. The participants in the study rinsed their mouths with coconut oil for 10 minutes each day for a week.
The theory is that oil pulling draws out the bacteria that live in the mouth while spitting the oil out removes the bacteria from the mouth. Some people use oils with antibacterial properties, such as coconut oil.
10. Avoiding processed and sugary foods
Eating starchy, processed foods too frequently may cause gingivitis and bleeding gums.
Starchy foods can stick to teeth and gums and break down into sugar. This action can lead to inflammation of the gums, bleeding, and an increase in decay.
Starchy, processed foods include refined bread, cakes, cookies, and potato chips.
11. Eating crunchy vegetables
Crunchy vegetables, such as celery and carrots, can help keep teeth clean between meals.
Their crunchy quality can help remove food residue from the teeth. Also, they contain low amounts of sugar and carbs, so they do not promote tooth decay or gum problems.
12. Eating more leafy greens
Kale and leafy greens are rich in essential nutrients.
Kale and leafy greens are rich in essential nutrients.
Leafy greens, such as kale, lettuce, and spinach, are excellent sources of various nutrients, including Vitamin K.
A vitamin K deficiency can affect the amount of time it takes for blood to clot, so people low in vitamin K may notice more bleeding than usual.
People who are prone to blood clots should ask a doctor about how much vitamin K they need in their diet.
Long-term treatment and prevention
The best way to avoid bleeding gums is to adopt a healthful lifestyle that prevents the diseases that cause bleeding gums.
People can often avoid and prevent bleeding gums and other gum problems by:
Practicing good oral health care, including brushing twice a day and flossing once a day.
Replacing toothbrushes every 3 to 4 months.
Seeing a dentist regularly.
Booking regular hygienist appointments for professional cleaning and tartar removal.
Seeing a doctor regularly to check for health problems that can contribute to gum problems, such as diabetes.
Avoiding smoking or working with a doctor to find ways to quit smoking.
Eating a healthful diet that includes plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables and limiting processed foods and foods with added sugars.
When to see a dentist
A person should check with their dentist if they notice changes in their gums, teeth, or mouth.
Pain, redness, or bleeding of the gums should not happen every day. If the problem arises frequently or does not go away with good oral hygiene practices, a dentist can check for early-stage gum disease and other issues.
See a healthcare professional for signs of infection, such as fever or swelling.
Vitamin deficiencies such as vitamin C or K, pregnancy, and certain medical conditions can also contribute to bleeding gums. People should see their doctor or dentist if the bleeding does not go away after trying to treat this symptom at home.
Regular dental visits can stop minor, early-stage gum disease from becoming more serious. Untreated gum disease can eventually lead to infection and tooth loss. A dentist can also look after the overall health of a person's mouth and spot bigger problems, such as the early stages of mouth cancer.





Comments