How Arab become Kingdom of Saudi Arabia

The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, KSA (Arabic: المملكة العربية السعودية, al-Mamlaka al-ʻArabiyya as-Suʻūdiyya), is an Arab country and the largest country of the Arabian Peninsula. It is bordered by Jordan on the northwest, Iraq on the north and northeast, Kuwait, Qatar, Bahrain, and the United Arab Emirates on the east, Oman on the southeast, and Yemen on the south. The Persian Gulf lies to the northeast and the Red Sea to its west. It has an estimated population of 27.6 million, and its size is approximately 2,150,000 square kilometres (830,000 sq mi).
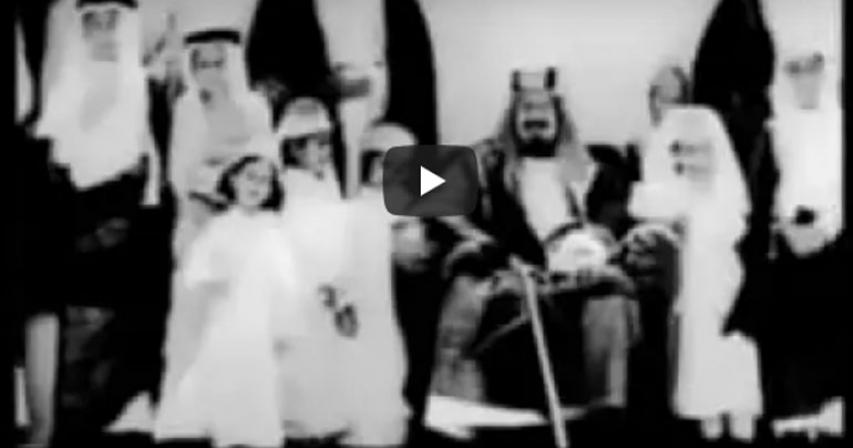
The Kingdom is sometimes called "The Land of the Two Holy Mosques" in reference to Makkah and Medinah, the two holiest places in Islam. In English, it is most commonly referred to as Saudi Arabia . The current Kingdom was founded by Abdul-Aziz bin Saud, whose efforts began in 1902 when he captured the Al-Sauds ancestral home of Riyadh, and culminated in 1932 with the proclamation and recognition of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, though its national origins go back as far as 1744 with the establishment of the First Saudi State.
Saudi Arabia is the world's leading petroleum exporter. Petroleum exports fuel the Saudi economy. Oil accounts for more than 90 percent of exports and nearly 75 percent of government revenues, facilitating the creation of a welfare state, which the government has found difficult to fund during periods of low oil prices. Saudi Arabia is often called, along with Russia, an energy superpower. Human rights groups such as Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch have repeatedly expressed concern about the state of human rights in Saudi Arabia, although these concerns have been dismissed by the Saudi government.
/ Source: youtube




Comments