About Saudi Arabia - State Of Saudi Arabia
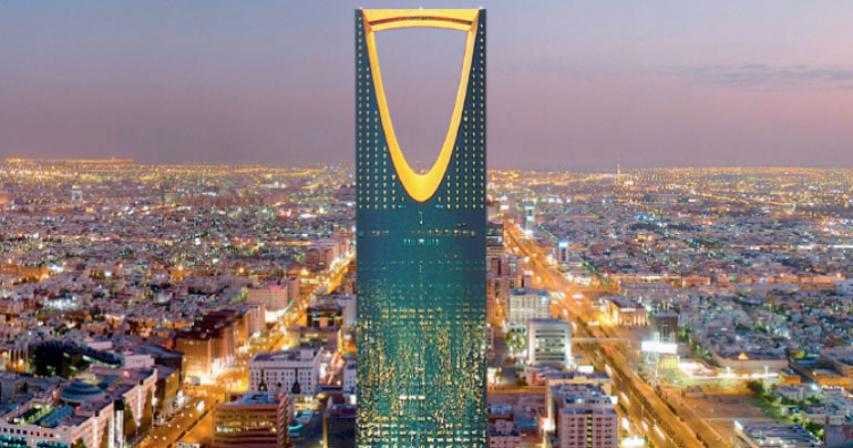

State of Saudi:
Saudi Arabia, officially known as the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is an Arab state in Western Asia constituting the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula. With a land area of approximately 2,150,000 km2 (830,000 sq mi), Saudi Arabia is geographically the fifth-largest state in Asia and second-largest state in the Arab world after Algeria. Saudi Arabia is bordered by Jordan and Iraq to the north, Kuwait to the northeast, Qatar, Bahrain, and the United Arab Emirates to the east, Oman to the southeast, and Yemen to the south. It is separated from Israel and Egypt by the Gulf of Aqaba. It is the only nation with both a Red Sea coast and a Persian Gulf coast, and most of its terrain consists of arid inhospitable desert or barren landforms.
The area of modern-day Saudi Arabia formerly consisted of four distinct regions: Hejaz, Najd, and parts of Eastern Arabia (Al-Ahsa) and Southern Arabia . The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia was founded in 1932 by Ibn Saud. He united the four regions into a single state through a series of conquests beginning in 1902 with the capture of Riyadh, the ancestral home of his family, the House of Saud. Saudi Arabia has since been an absolute monarchy, effectively a hereditary dictatorship governed along Islamic lines. The ultra-conservative Wahhabism religious movement within Sunni Islam has been called "the predominant feature of Saudi culture", with its global spreading largely financed by the oil and gas trade. Saudi Arabia is sometimes called "the Land of the Two Holy Mosques" in reference to Al-Masjid al-Haram (in Mecca), and Al-Masjid an-Nabawi (in Medina), the two holiest places in Islam.
Petroleum was discovered in 1938 and followed up by several other finds in the Shia-majority Eastern Province. Saudi Arabia has since become the world's largest oil producer and exporter, controlling the world's second largest oil reserves, and the sixth largest gas reserves. The kingdom is categorized as a World Bank high-income economy with a high Human Development Index, and is the only Arab country to be part of the G-20 major economies. However, the economy of Saudi Arabia is the least diversified in the Gulf Cooperation Council, lacking any significant service or production sector (apart from the extraction of resources). A monarchical autocracy, Saudi Arabia has the fourth highest military expenditure in the world,and in 2010–14, SIPRI found that Saudi Arabia was the world's second largest arms importer. Saudi Arabia is considered a regional and middle power. In addition to the GCC, it is an active member of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation and OPEC
Economic and social development:
Saudi Arabia's command economy is petroleum-based; roughly 75% of budget revenues and 90% of export earnings come from the oil industry. It is strongly dependent on foreign workers with about 80% of those employed in the private sector being non-Saudi. Among the challenges to Saudi economy include halting or reversing the decline in per capita income, improving education to prepare youth for the workforce and providing them with employment, diversifying the economy, stimulating the private sector and housing construction, diminishing corruption and inequality.
The oil industry comprises about 45% of Saudi Arabia's nominal gross domestic product, compared with 40% from the private sector .Saudi Arabia officially has about 260 billion barrels of oil reserves, comprising about one-fifth of the world's proven total petroleum reserves.
In the 1990s, Saudi Arabia experienced a significant contraction of oil revenues combined with a high rate of population growth. Per capita income fell from a high of $11,700 at the height of the oil boom in 1981 to $6,300 in 1998. Taking into account the impact of the real oil price changes on the Kingdom's real gross domestic income, the real command-basis GDP was computed to be 330.381 billion 1999 USD in 2010. Increases in oil prices in the aughts[peacock term] helped boost per capita GDP to $17,000 in 2007 dollars (about $7,400 adjusted for inflation), but have declined since oil price drop in mid-2014.
OPEC (the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries) limits its members' oil production based on their "proven reserves." Saudi Arabia's published reserves have shown little change since 1980, with the main exception being an increase of about 100 billion barrels between 1987 and 1988. Matthew Simmons has suggested that Saudi Arabia is greatly exaggerating its reserves and may soon show production declines.
The government has also made an attempt at "Saudizing" the economy, replacing foreign workers with Saudi nationals with limited success.
Saudi Arabia has had five-year "Development Plans" since 1970. Among its plans were to launch "economic cities" (e.g. King Abdullah Economic City) to be completed by 2020, in an effort to diversify the economy and provide jobs. As of 2013 four cities were planned. The King has announced that the per capita income is forecast to rise from $15,000 in 2006 to $33,500 in 2020. The cities will be spread around Saudi Arabia to promote diversification for each region and their economy, and the cities are projected to contribute $150 billion to the GDP.
In addition to petroleum and gas, Saudi also has a small gold mining sector in the Mahd adh Dhahab region and other mineral industries, an agricultural sector (especially in the southwest) based on dates and livestock, and large number of temporary jobs created by the roughly two million annual hajj pilgrims.
Location:
Saudi Arabia is positioned in the Middle East, a recognized geographical region of southwestern Asia, and is situated in both the northern and eastern hemispheres.Saudi Arabia is bordered by the countries of Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, UAE, and Yemen, as well as the Red Sea, Persian Gulf and Gulf of Aqaba.
Topographic Features:
- Saudi Arabia is, for the most part, an uninhabited desert land, which includes the Rub' Al Khali Desert, the largest mass of sand in the world, and the An-Nafud Desert - where sand dunes often exceed 100 ft. in height.
- The land (desert) rises into hills and mountains in the west and southwest, along the edges of the Red Sea. Mountain ranges include the Hejaz in the northwest, and the Azir in the southwest.
- Saudi Arabi's highest point is Jabal Sawda' which peaks at 10,279 ft. (3,133 m).
Land Area:
The value for Land area (sq. km) in Saudi Arabia was 2,149,690 as of 2015. As the graph below shows, over the past 54 years this indicator reached a maximum value of 2,149,690 in 2015 and a minimum value of 2,149,690 in 1961.
Population:
- The current population of Saudi Arabia is 32,317,921 as of Friday, October 7, 2016, based on the latest United Nations estimates.
- Saudi Arabia population is equivalent to 0.43% of the total world population.
- Saudi Arabia ranks number 41 in the list of countries by population.
- The population density in Saudi Arabia is 15 per Km2 (39 people per mi2).
Capital City:
Riyadh
Official Language:
Arabic is the official language of Saudi Arabia, but English is widely spoken. It is used in business and is a compulsory second language in schools. Among the non-Saudi population, many people speak Urdu, the official language of Pakistan, and other Asian languages such as Farsi and Turkish.
Climate:
With the exception of the province of Asir on the western coast, Saudi Arabia has a desert climate characterized by extreme heat during the day, an abrupt drop in temperature at night, and very low annual rainfall.
Major Towns:
- Riyadh
- Jeddah
- Mecca
- Medina
...[ Continue to next page ] / Source: the-wau





Comments